IAME – Decentralized Identification System Built For Blockchain Ecosystems

Blockchain is the world’s leading software platform for digital
assets. Offering the largest production block chain platform in the
world, we are using new technology to build a radically better financial
system. A decentralized identification system that would allow parties
performing blockchain transactions to verify, on a primary level, the
identity of each other without having to disclose non-essential
sensitive personal information to the counterparties; and on a secondary
level the source of the Cryptocurrencies in the transaction.
IAME is a professional system for that will enable Blockchain
identify verification by parties who are involved in executing
transactions on Blockchain platform to confirm it’s identify at any
level whether primary or secondary. It is built specifically to serve
peer -2- peer exchanges in Blockchain.
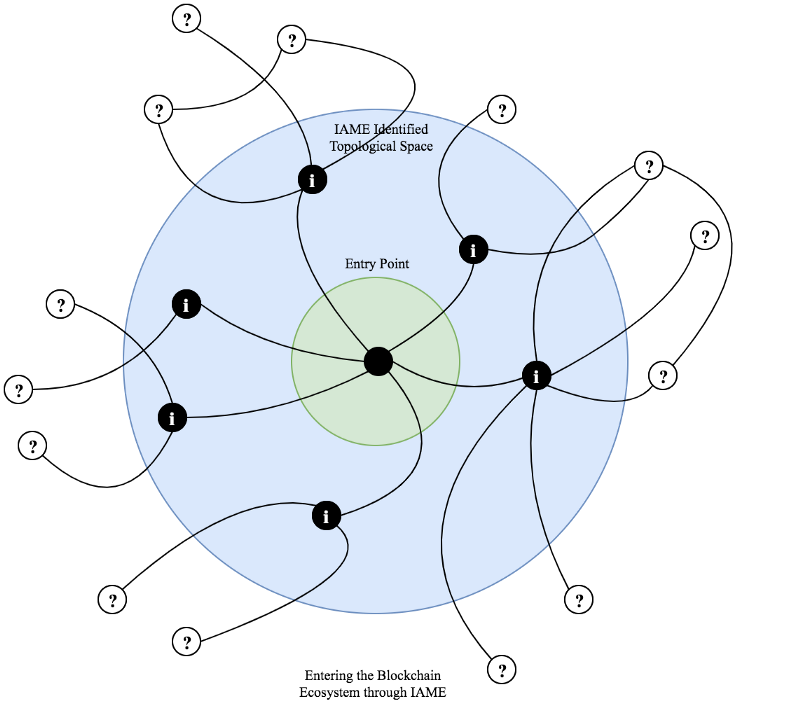
The Current Challenge
Solution That IAME Proposes
The applying of present verification on protocols on the advanced
block-chain is not well matched with the ideals of decentralization.
Though, the rule of anonymity is at odds with narrow needs for
anti-money laundering regulations. Thus, there’s a need to get to a
compromise. This’ll able the 2 sides to come to a symbiotic being where
everybody gets what they require.
To land a working solution, the IAME platform suggests reinventing
the verification procedure. Thus, it advises an adjustment from a
wholesome it to a fragmented platform. There’ll be clearly verified
topological areas, which can be applied as a mark of entry of lawmakers.
The IAME platform will thus seek out to resolve the problem of
anonymity without stopping the block-chain revolution.
By making a fragmented verification system, consumers of the
block-chain can be capable to validate their address with no having
entrusted sensitive data to each party with that they interact. However,
it can remain help lawmakers confirmation user to make sure they’re not
connecting to money laundering.
The IAME Identification Network
The proposed IAME Identification Network would have a core that consists of:
The proposed IAME Identification Network would have a core that consists of:
- a client,
- an allocation server,
- a validation server,
- a writeable blockchain, and
- an identity server.
Each component would carry out specific functions that can be
demonstrated in 2 processes – a validation process, and an
identification process.
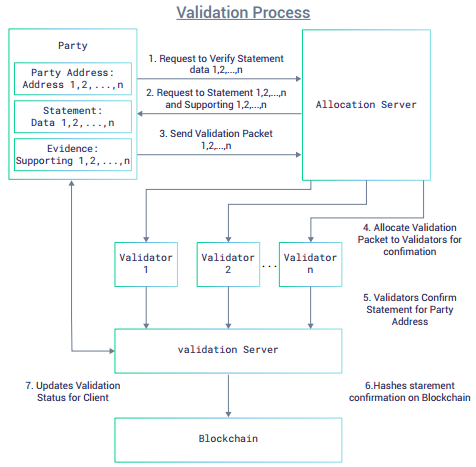
- The validation process would be the operation through which the client would have her/his information validated by third-party validators. The process is as shown below:
- Upon request, statements and their corresponding supporting information would be fragmented at the client level and encrypted into validation packets to be sent to the allocation server.
- The allocation server would control the random allocation of validation packets to third-party validators, who would return the result of their validations to the validation server.
- Once the above is completed, the validation server would evaluate the validations from the third-party validators, and hash numeric or boolean confirmations paired to specific statements on a designated writeable blockchain.
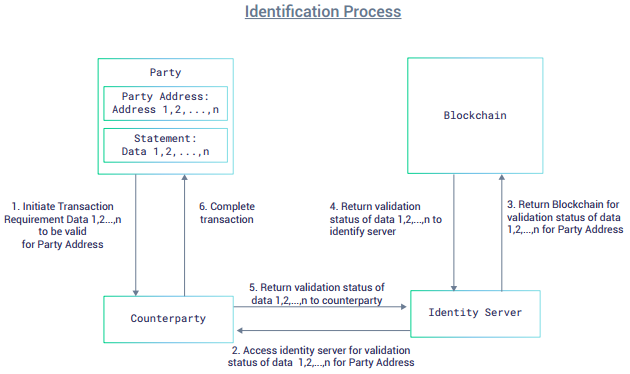
For a counterparty to transact with a client, an identification
process has to be completed. This process is based on the counterparty’s
own specific requirements.
- Assuming that the counterparty requires Data 1,2,.. n to be validated for a specific transaction with a party, the counterparty sends a request to the Identity Server for the validation status of Data 1,2,.. n.
- The Identity Server reads the blockchain for validation status of Data 1,2,..n for the party, and returns the validation data to the counterparty, and from thereon the counterparty can complete the transaction.
While the IAME Identification Network would not be a bypass for
data sharing between transactional counterparties, it would serve to
segregate the distribution and validation of non-essential sensitive
personal information.
Third Party Validation
Pursuant to the concept of the IAME fragmented identification system, there is a requirement for a system of decentralised third-party validators under the rational that an identification validation conducted by a multitude of third-party validators is more dependable and less susceptible to the risk of fraud than an identification validation conducted by a single institution or party.
Pursuant to the concept of the IAME fragmented identification system, there is a requirement for a system of decentralised third-party validators under the rational that an identification validation conducted by a multitude of third-party validators is more dependable and less susceptible to the risk of fraud than an identification validation conducted by a single institution or party.
The solution we propose is a symmetric game model that will
encourage truthful validation that is analogous to the Byzantine Fault
Tolerance – the Trial Algorithm.
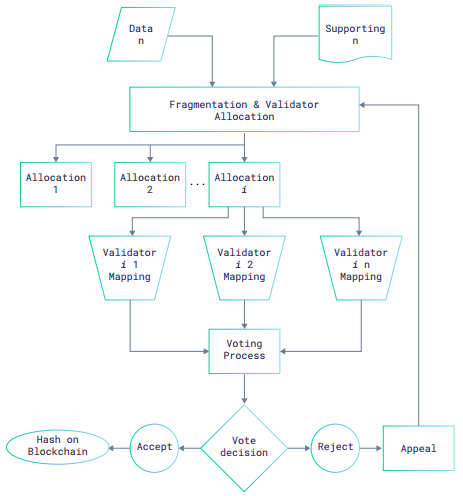
Aspects of the Trial Algorithm:
- Each statement and their corresponding supporting information are processed as fragments ( “Evidence” );
- Evidence is validated not by single third-party validators ( “Jury” ), but by a Jury (a “Tribunal” );
- Each jury validates in a designated method on whether the Evidence matches the statements
- The Tribunal validations are counted and a majority rule consensus is reached
- If there is a non-majority consensus on an evidence, the evidence is sent through a second tribunal ( “Appeal” )
- If the appeal jury votes to a majority consensus identical to the initial tribunal,the decision is upheld, or else the initial tribunal decision is rejected
An Identification System for Blockchain P2P Transaction
With a functional IAME Identification Network, the primary
application would be the facilitation of blockchain P2P transaction,
such as online merchant transactions. Taking into consideration a simple
online purchase where a customer purchases a physical good from an
online merchant with Cryptocurrencies, the amount of personal data that
is communicated from the customer to the merchant can be segregated into
two categories: essential to the transaction and non-essential to the
transaction.
Essential information would be a name and an address without which the transaction and the delivery of the good cannot occur
Non-essential information would include, for example, an identity
document to prove the name of the customer, a utility bill to prove that
the address belongs to the customer, and the specific date of birth of
the customer
Conclusion
Making use of the projected IAME credentials Network lay out in
this platform, we hunt to determine the dilemma parties face in
blockchain transactions by making sure to spot themselves with a whole
host of counterparties, whereas both preserving the obscurity of the
transacting party, and gratifying the need for counterparties to conduct
a certain level due diligence on clients.
The IAM Token
To operate the IAME Identification Network, a functional token will
be issued, known as the IAM Token, which would operate as a validation
token to initiate confirmation requests for validation packets on the
IAME Identification Network.
The value of the IAM Token would be, in essence, determined by 2 factors:
- The cost of validation, which would be proportional to the financial cost of hashing the requested amount of data on the designated blockchain, setting a price floor for the token
- Market demand, which would be proportional to the demand for blockchain identification based on the IAME Identification Network
IAME Cap
Minimum Cap1,000,000 USD
Maximum Cap25,000,000 USD
Minimum Cap1,000,000 USD
Maximum Cap25,000,000 USD


Advisors


Press

For more information please visit here:
AUTHOR ; meliamel
mybitcointalk ; https://bitcointalk.org/index.
Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar